Showing posts with label SQL Server. Show all posts
Showing posts with label SQL Server. Show all posts
Sunday, 30 May 2021
Friday, 3 May 2019
Check SQL Database size
SQL Query to calculate database size
Below is the query to check the disk space.
SELECT sys.databases.name as DBName,
CONVERT(VARCHAR,SUM(size)*8/1024)+' MB' AS [Disk Size]
FROM sys.databases
JOIN sys.master_files
ON sys.databases.database_id=sys.master_files.database_id
GROUP BY sys.databases.name
ORDER BY sys.databases.name
How to check log size and clear log
DBCC SQLPERF(logspace)
DBCC LOGINFO
Below is the query to shrink the log. The first parameter is the log name. you can get the name by pressing the right click on the database and click Properties and then select Files Tab. The second parameter is database size in MB
Friday, 23 October 2015
Change Rows to Columns - Pivot in SQL Server
PIVOT
In this article, we will discuss PIVOT keyword in Sql Server. Pivot is responsible to convert Rows to Columns in Sql Server.
Let's take the example.
Step 1: Declare SQL table and add some dummy data
DECLARE @ScoreTable TABLE
(
MatchType VARCHAR(50),
Year INT,
Score INT
)
INSERT INTO @ScoreTable VALUES('OneDay',2012,1000)
INSERT INTO @ScoreTable VALUES('Test',2012,2200)
INSERT INTO @ScoreTable VALUES('OneDay',2013,800)
INSERT INTO @ScoreTable VALUES('Test',2013,370)
INSERT INTO @ScoreTable VALUES('Test',2014,1100)
Step 2: Run the Select query and see the default data
This is not mandatory step. However, just check you dummy data.
SELECT * FROM @ScoreTable
In above query, you can see we have 3 columns. MatchType, Year and Score.
We will change Year Rows data in Columns.
Step 3: Write query to covert rows to columns
SELECT * FROM @ScoreTable
PIVOT(SUM(Score)
FOR Year IN ([2012], [2013],[2014])) AS PVTTable
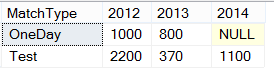
In above snapshot, you can see query changed year to columns and score under each column.
This is all about the article. I hope you like it.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Azure Function - In-process model vs Isolated worker model
In-process model Your function code runs inside the same process as the Azure Functions runtime Uses the WebJobs SDK . [FunctionName(...
-
This error normally occurred when you created a report on one SQL version and deploying/opening on another SQL version. I've created ...
-
OR The attempt to publish the ZIP file through failed with HTTP status code Unauthorized. When you get this error while publishing the Websi...
-
Typically, PowerBIEntityNotFound indicates that the requested resource (report, dataset, or workspace) could not be found under the access t...








